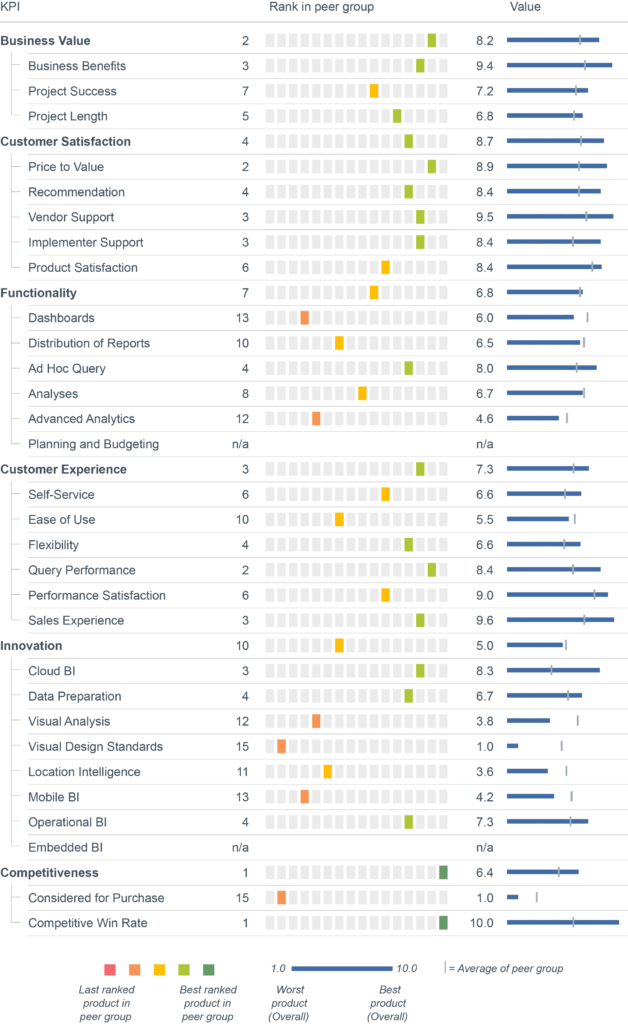
Founded in 2003, Tableau emerged from scientific research at Stanford University and is now among the best-known BI & analytics brands worldwide. Following its acquisition by Salesforce in 2019, the company continued to operate largely as an independent BI vendor. With the recent launch of its Tableau Next platform, Tableau has built on Salesforce’s investments in data, agentic AI and trust layers to advance its vision of empowering all users to analyze data and take informed action based on trusted insights. Tableau Next aims to deliver a new approach to business intelligence by using AI-powered autonomous agents to analyze data, proactively share insights and take action to enable humans and AI agents to work together from data to insights to action. Besides the visualization tool, Tableau Next includes Tableau Semantics, a semantic layer with AI-supported modeling features, to deliver actionable insights into users’ workflows.
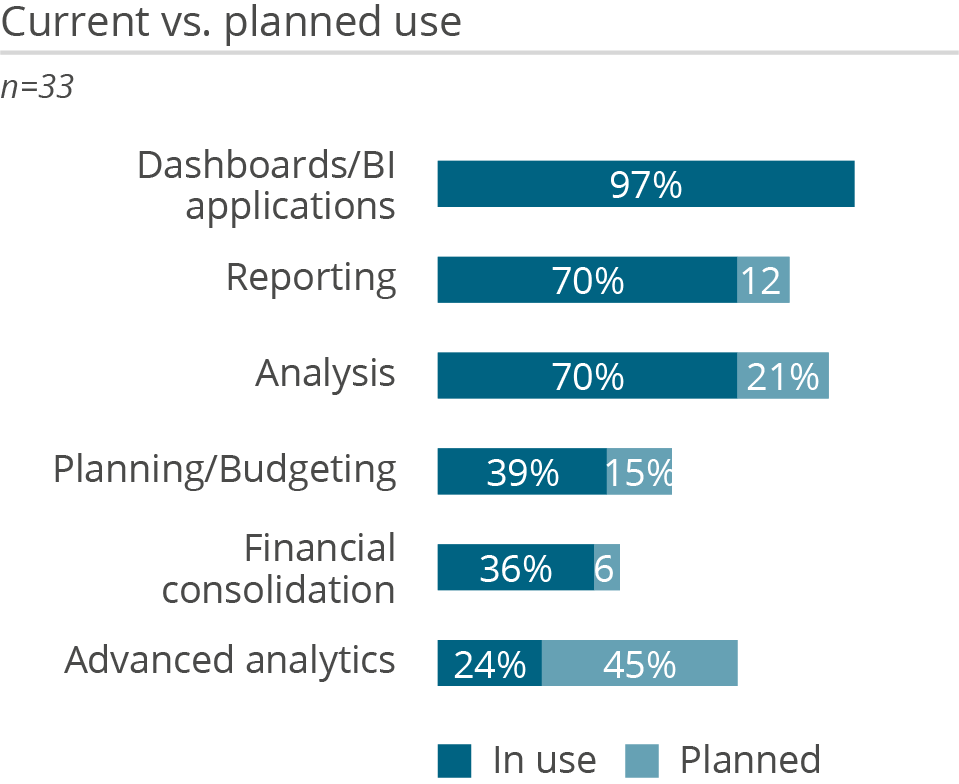
Tableau remains committed to developing software that requires little training and allows business users to interpret data, mostly by means of interactive visualization and making decisions based on analytics. The intuitive user interface, built-in intelligence and option for in-memory data processing to optimize performance all contribute to the popularity of this solution for visual analysis, dashboards and data discovery. The product offers solid support for analysts through various features such as one-click analyses, data explanations and highlighting anomalies in data.
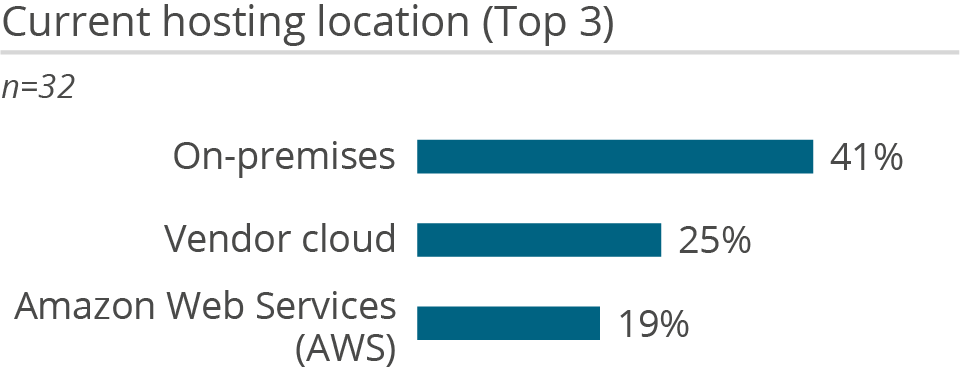
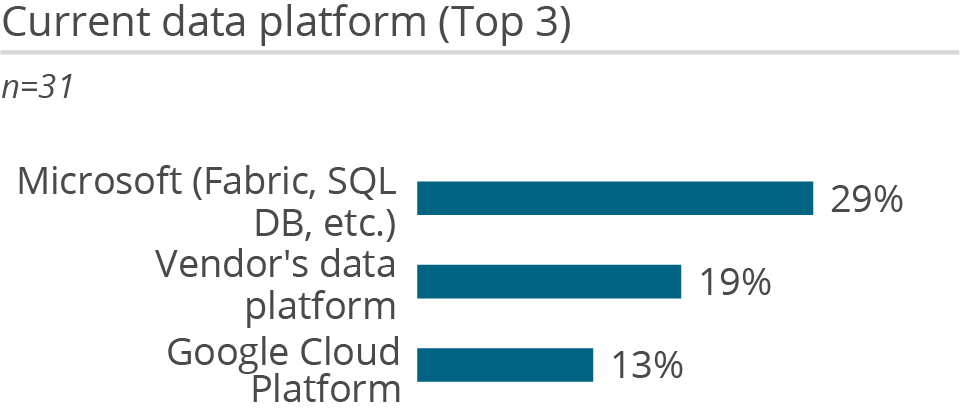
Tableau’s openness to a variety of data sources is one of its strengths, as it is not necessary to rehost data to use Tableau. The solution allows users to query data live from different data sources, to combine data from across these sources, or to move the data into its own ‘Hyper’ in-memory database for analysis. To ensure performance, Tableau optimizes live queries to generate the most efficient SQL and converts it to source-native dialect. Moreover, to reduce data movement, the product utilizes pushdown optimizations and its federated query cost-based optimizer. The vendor aims to do processing as close to the data as possible, even across different sources.
Data preparation in Tableau can be quick as many manipulations can be made directly while analyzing data, enabling a truly iterative approach to data discovery. With Tableau Prep, data preparation has been enhanced with deeper functionality and a more visual approach with recommendations for data shaping, profiling and enhanced traceability. Tableau Prep transformation flows can be created either on the desktop or via Tableau Cloud and may be scheduled and orchestrated on the server to operationalize data preparation tasks. Data science scripts such as R and Python can be dynamically integrated into Tableau’s data prep and analysis features.
With regards to AI, the Agent feature uses the Einstein Trust Layer and leverages LLMs to support customers with natural language capabilities (e.g., via creating calculations or suggesting visualizations). Tableau Pulse is a natural-language, metrics-based feature equipped with AI functionality to guide users to needed insights and assist in interpreting them. Additionally, the auto-ML capabilities of Salesforce’s Einstein Discovery integrated with Tableau provide advanced predictions and recommended next best actions.
The vendor is actively pursuing the expansion of its active community. Tableau Exchange is a platform for partners to provide a growing catalog of offerings including Viz Extensions (recently announced), connectors and accelerators (prebuilt dashboards).