Mobile Business Intelligence: What it is and how it works
Are you looking for further assistance on this topic? You will find it here.
Nowadays, companies are under increasing pressure to make better decisions faster. Mobile business intelligence (BI) systems are deployed both to keep pace with rivals and to try to gain an advantage over the competition. This simply cannot be effective if the information used is out of date.
The pace of business has now changed, leading to an inevitable shift in decision-making processes. The spread of internet-enabled mobile devices has reached the point at which they should now be considered as a major contributor to rapid decision support.
What is Mobile BI?
The definition of mobile BI refers to the access and use of information via mobile devices. With the increasing use of mobile devices for business – not only in management positions – mobile BI is able to bring business intelligence and analytics closer to the user when done properly. Whether during a train journey, in the airport departure lounge or during a meeting break, information can be consumed almost anywhere and anytime with mobile BI.
Mobile BI – driven by the success of mobile devices – was considered by many as a big wave in BI and analytics a few years ago. Nowadays, there is a level of disillusion in the market and users attach much less importance to this trend.
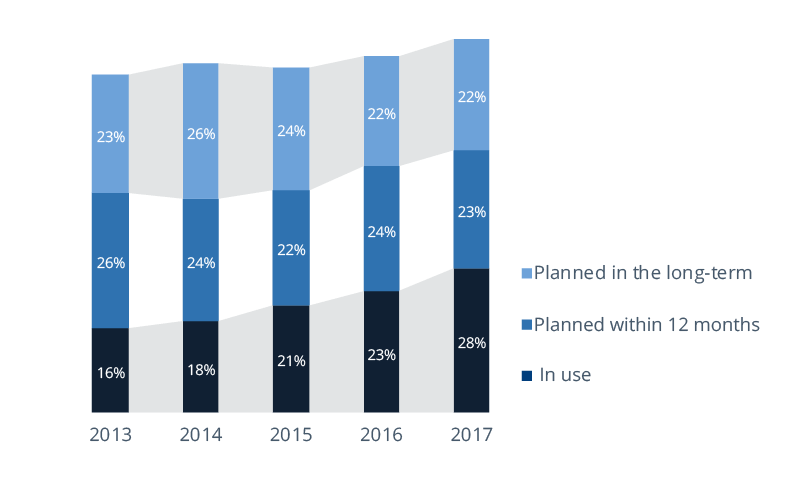
Survey data from BARC’s BI Trend Monitor 2018 shows that market penetration is growing relatively slowly: in 2017, 28 percent of BI users stated that mobile BI is already in use in their company (up from 23 percent in 2016, 21 percent in 2015, 18 percent in 2014, and 16 percent in 2013 and 2012).
Mobile BI Usage
One of the major problems customers face when using mobile devices for information retrieval is the fact that mobile BI is no longer as simple as the pure display of BI content on a mobile device. Moreover, a mobile strategy has to be defined to cope with different suppliers and systems as well as private phones.
Besides attempts to standardize with the same supplier, companies are also concerned that solutions should have robust security features. These points have led many to the conclusion that a proper concept and strategy must be in place before supplying corporate information to mobile devices.
Benefits of mobile BI
The first major benefit is the ability for end users to access information in their mobile BI system at any time and from any location. This enables them to get data and analytics in ‘real time’, which improves their daily operations and means they can react more quickly to a wider range of events.
The integration of mobile BI functions into operational business processes increases the penetration of BI within organizations and often brings benefits in the form of additional information.
This speeds up the decision-making process by extending information and reducing the time spent searching for relevant information. With this real-time access to data, operational efficiency is improved and organizational collaboration is enforced.
Overall, mobile BI brings about greater availability of information, faster reaction speed and more efficient working, as well as improving internal communication and shortening workflows.
Finally, with the provision of proper mobile applications to all mobile device users, information can be used by people who previously did not use BI systems. This in turn leads to a higher BI penetration rate within companies.
Mobile BI technology
A variety of mobile devices can be used to display and actively work with information. Smartphones, tablets and wearables from brands such as Apple, Samsung, HTC and BlackBerry are the most common today.
A significant difference between these types of device is obviously the size of the screen, which also affects mobile BI. For instance, tablets are comparable to small notebook computers, and are typically not subject to the extreme constraints of the small screen of a mobile phone.
Thus, they offer more space to display content such as dashboards and reports, business data and KPIs compared to the smaller screen of mobile phones. Although BI applications can theoretically run on both tablets and mobile phones, they are not equally well suited to all types of BI. For example, interactive data visualizations require more screen space than displaying KPIs within a table.
There are various ways to implement content on mobile devices. The most common we see in the marketplace are:
- Provision of PDF reports to a mobile device
- Website (HTML rendering), partly using proprietary technologies (Flash, Silverlight)
- HTML5 site
- Connection of a native application with HTML5 (hybrid application)
- Native application
In principle, any BI vendor that can create a PDF or render in HTML (and almost all of them can) can say it supports mobile BI. Most mobile devices include a web browser that can access almost any web page to an acceptable degree of quality. The exception here is when proprietary technologies – which require additional software to display – are used.
In the case mentioned, BI developers must check how their content renders on a mobile device when creating reports and other visualizations. This means designing their application specifically for mobile use. The main advantage of this is its independence from device types (except when using proprietary technologies), since the content can be consumed on all devices.
Another interesting trend among many software developers is the HTML5 client. BI content is displayed in the browser as previously described, but with several improvements. HTML5 enables Rich Internet Application (RIA) content to be projected across all types of mobile devices without relying on proprietary standards and without having to deal with their disadvantages.
This technology is favored by software manufacturers, and not just because of its browser and operating system capabilities. The end user also benefits by being able to use it without having to install it. Unlike traditional HTML rendering, clients developed in HTML5 also provide some mobile-optimized navigation controls and functions such as zooming, pinching and double-tapping.
In addition, HTML5 can be merged with the features of a native mobile application into a so-called “hybrid” form. This generally refers to a web application that can be downloaded as an app and installed on the device, but at its core includes a web viewer. For this reason, hybrids are often hard to distinguish from native apps. This hybrid category essentially supports more of the native features of the mobile device than a pure HTML5 client, but fewer than a native application.
The “native” application type is the most expensive way for software manufacturers to support mobile BI because the software has to be tailored to the operating system (OS) of the mobile device. Native apps are typically downloaded and installed.
The advantage of these products lies in their support of device-specific properties, such as the use of cache and navigation controls like “swipe” on the iPhone or iPad. Although the creation of native apps requires effort on the customer and vendor side, they enable interactive and enhanced use of analytics content.
For instance, device functions such as voice recognition can be coupled with the software’s natural language generation capabilities to query data ad hoc based on speech. Moreover, app developers are able to use sensors such as GPS to guide a customer to an article which is calculated to be potentially relevant to him. The more operational use and interaction with information that is required, the better the mobile OS support has to be.
In general, the trend in mobile BI apps is veering towards knowledge generation rather than pure content consumption. Analysis and manipulation as well as input options for data are increasingly supported these days. Meanwhile, forecasts based on past data can be statistically calculated and directly reused on mobile devices.
In our opinion, information should be updated as often as the reader needs it (sometimes even in real time). Especially in operational scenarios, decision-makers often have to react instantly to insights from data or changes in circumstances.
Importance of Mobile BI in 2018 (n=2,637)
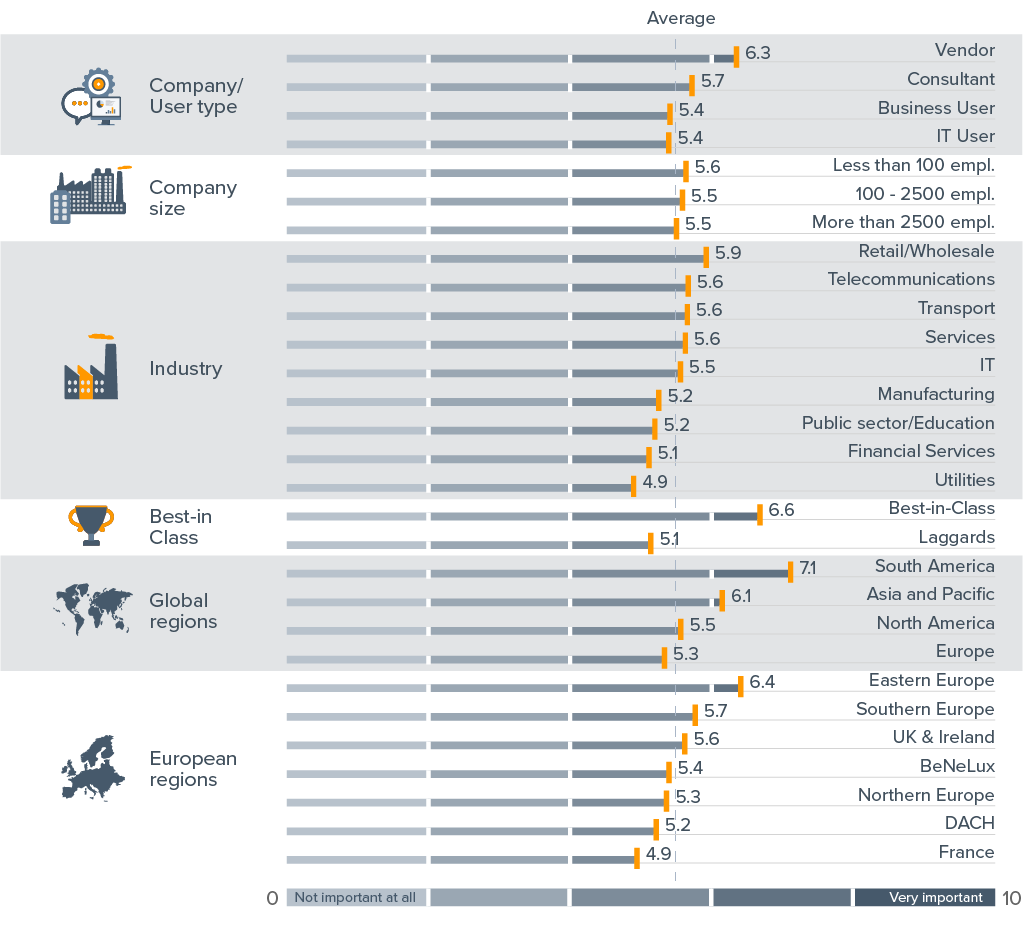
Best-in-class companies attach much more importance to mobile BI than other companies.
Since 2016 there has been a downturn for nearly all categories, except Best-in-class, Laggards, Eastern Europe, the DACH region and the transport and telecommunications sector.
Mobile BI tools
The requirements and expectations of mobile BI are increasing so the selection of the right product is key to guaranteeing the maximum return on investment.
Since providers are strongly oriented towards the most popular operating systems, they are also aligning their product portfolios for mobile BI.
As well as vendors developing mobile BI solutions for their own BI software, there are more and more companies selling platform-independent systems. Most of them are specialist manufacturers who use the BI systems of popular providers such as IBM, SAP or Microsoft to extract information. Data is then integrated, processed and displayed using their own technologies. This type of mobile software is especially suitable for companies that use multiple BI systems.
Challenges of Mobile Business Intelligence
Despite all the good things that mobile BI solutions bring, organizations are also exposed to a number of challenges when trying to achieve a successful platform adoption:
- Regardless of the delivery option, customers must consider usability. Displaying familiar content in a mobile browser (even as HTML5) does not necessarily mean that it can be used intuitively. Companies and app developers should take great care in designing the user interface to ensure the app’s acceptance, especially in operational scenarios where workers may not be accustomed to using BI
- When implementing a mobile BI solution, security and privacy may pose problems. Companies have to make sure they implement a strong security configuration in order to protect sensitive business and user data. Furthermore, the mobile strategy should be aligned with existing security procedures.
- Mobile devices can easily be hacked, lost or stolen. Using mobile BI may consequently put sensitive or confidential information at greater risk of being breached.
- Due to the limited screen size of mobile devices, the design of mobile BI applications presents new challenges to developers. Each device and browser works differently.
BARC recommendations
In our experience, the most successful mobile deployments are those in which a mobile strategy has already been defined and the needs of the mobile workforce are carefully addressed with the mobile application. Simply copying an existing web dashboard to a mobile environment may work for some users, but for most it will not be a successful approach. There are several ways of providing information to users.
Typical project steps are as follows:
- Determination of the requirements for mobile usage scenarios (e.g., functionality, level of interaction with the system and device sensors required)
- Definition of a mobile BI strategy (clarification of components such as architecture, security and user roles)
- Mobile device selection (after thorough consideration of whether to use smartphones or tablets, or another device)
- Thorough evaluation and selection of the mobile BI application, analogous to a normal business software selection process
- Integration into the existing software and hardware landscape
- Mobile application development in cooperation with the people who will be using it
Don’t forget that software is only as good as its users think it is!









